Universal Cell Platform(TyUCell®)refers to the use of gene editing technology to transform allogeneic immune cells to eliminate immune rejection.
lEARN MORE TyUCell®The Quickin CAR-T Platform(Quickin CART®) generates T cell products with gene knockout and stable integration of CAR cassette in one step through CRISPR gene editing technology.
lEARN MORE Quickin CART®Enhanced T cell Platform(HyperTCell®), including HyperCART ® , are mainly to solve the global highlighted problem in solid tumor therapy through genetic modification of T cells.
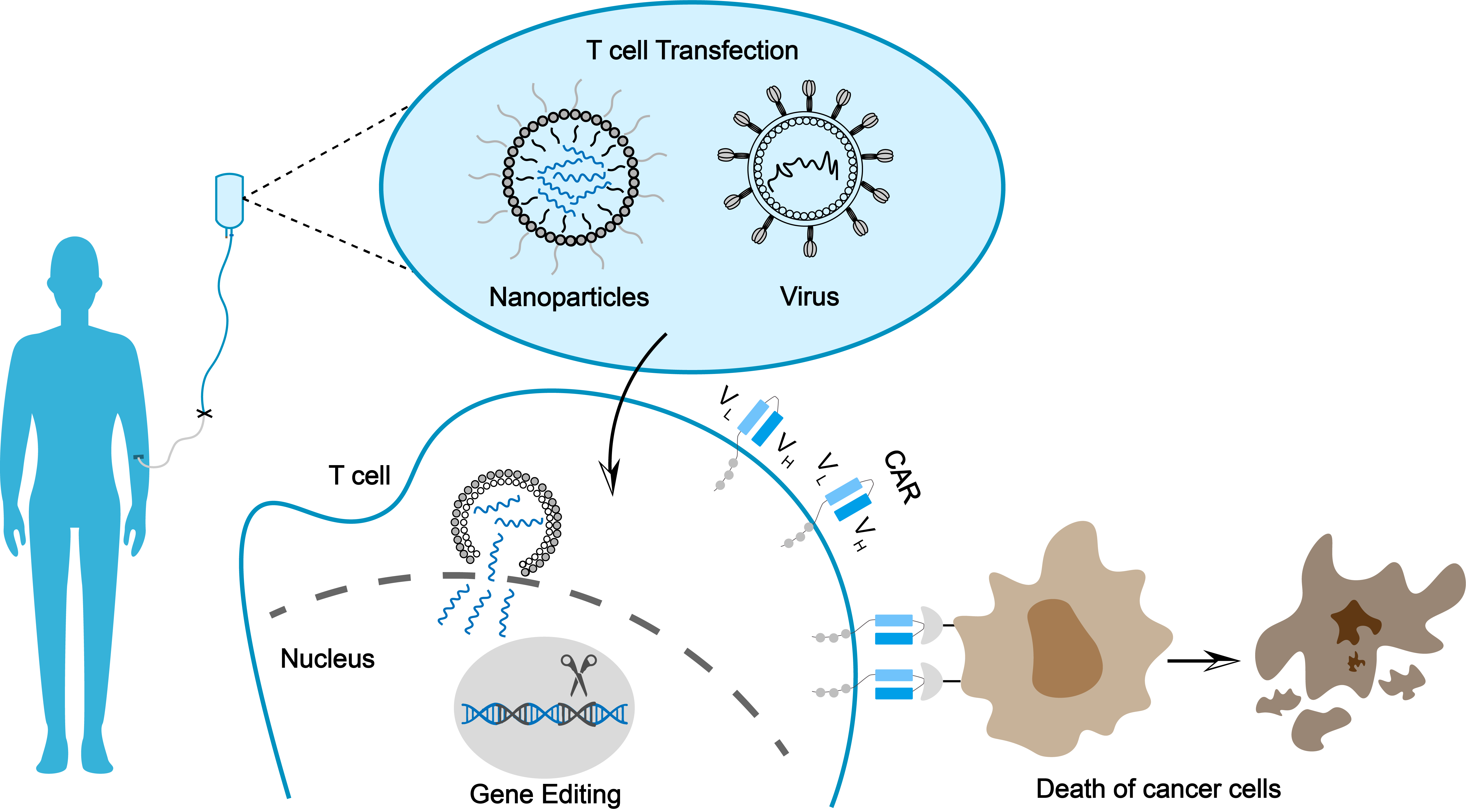
lEARN MORE HyperTCell®The in vivo CAR-T platform represents an innovative approach that enables direct in vivo delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) genes into a patient’s T cells, thereby generating functional CAR-T cells internally.
lEARN MORE In vivo CAR-TThe in vivo CAR-T platform represents an innovative approach that enables direct in vivo delivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) genes into a patient’s T cells, thereby generating functional CAR-T cells internally. Specifically, viral or non viral vectors (such as LNP lipid nanoparticles) are used to specifically deliver the gene fragment encoding car to T cells, which can achieve rapid, instantaneous and controllable therapeutic effect without going through the complex process of traditional in vitro separation and expansion of T cells. This platform has the core advantages of greatly simplifying the process, significantly reducing the production cost and greatly improving the accessibility. It provides a new technical path and solution for tumor and autoimmune diseases.